Artificial intelligence and new computational methods are revolutionizing scientific research. One of the fields where their influence and impact is most evident is in cancer, where the amount of available data is constantly accumulating. To explore and share the latest advances in these areas, the Barcelona Supercomputing Center – Centro Nacional de Supercomputación (BSC-CNS) and Columbia University, with […]

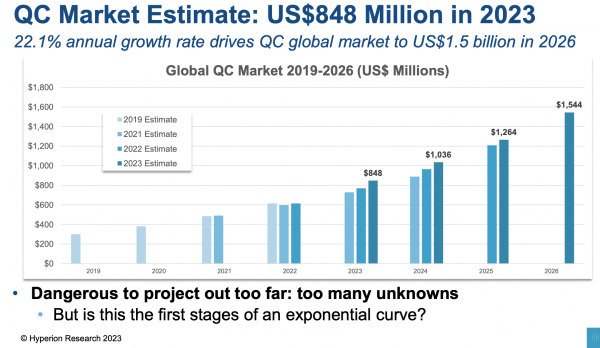
Few markets as small as the quantum information sciences market generate as much lively discussion. Hyperion Research pegged the worldwide quantum market at $848 million for 2023 and expects it to reach ~$1.5 billion in 2026, according to its annual quantum computing (QC) market update presented at the Q2B Silicon Valley conference held in Santa […]

While the IBM Quantum Summit and the QC Ware’s Q2B Silicon Valley conference dominated last week’s news flow, there was no shortage of other quantum news emerging. Here’s a brief recap of highlights. Let’s start with work published in Science last Thursday in which two groups of researchers, one from Harvard University and another from […]

Women in High Performance Computing (WHPC), in collaboration with Alces Flight, is proud to unveil the ‘Move the Needle’ project, a initiative aimed at fostering workplace inclusivity in the High Performance Computing industry. The ‘Move the Needle‘ project, a year-long event, is dedicated to tracking actions and fostering accountability in the realm of diversity and […]

NCSA has long supported women in High-Performance Computing (HPC). To that end, the Center served as an academic sponsor of the annual Grace Hopper Celebration of Women in Computing (GHC) in Orlando and sent team members from several areas to this year’s conference. Named after famed computer scientist Grace Hopper and organized by the Anita Borg Institute for Women and […]

Nov. 8, 2023 — Two teams that include scientists from U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Argonne National Laboratory have been named finalists for the Association for Computing Machinery 2023 Gordon Bell Prize. This image shows the individual pins in a full-core nuclear reactor simulation, one of the first ever done. Image: Argonne National Laboratory. Both […]

This year’s fantastic Supercomputing 2023 was back in full form. Attendees seemed to be glad that the show was back in Denver, which was a preferred destination over last year’s show in Dallas. The post Supercomputing 2023: Odds and Ends from the Show appeared first on HPCwire.
Nov. 16, 2023 — Princeton University has launched a new Ph.D. program in Quantum Science and Engineering, providing graduate training in an emerging discipline at the intersection of quantum physics and information theory. Credit: Princeton University This new field of quantum information science may enable fundamentally new technology, including new types of computers that can […]

Fermionic atoms are atoms that obey the Pauli exclusion principle, which means that no two of them can occupy the same quantum state simultaneously. This makes them ideal for simulating systems where fermionic statistics play a crucial role, such as molecules, superconductors and quark-gluon plasmas. The post Scientists in Austria Unravel the Potential of Fermions […]

Water, despite its simple molecular structure, behaves in ways that have long puzzled scientists. While it is universally recognized as essential to life, water’s anomalous properties present unique challenges for computational modeling. But in a groundbreaking study published in Nature Communications, scientists from UC San Diego have made a major stroke in simulating water’s phase […]